285. Inorder Successor in BST
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node p is the node with the smallest key greater than p.val.
Example 1:
Input: root = [2,1,3], p = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of TreeNode type.
Example 2:
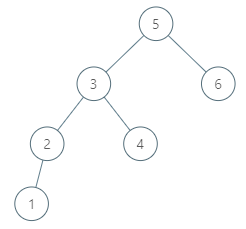
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer is null.
Note:
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return
null. - It's guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
---
Related problems
---